Photo credit: iStock/Victoria Popova
Positive Effects on Muscle Tissue
A study by Aussieker T et al. (2025) provides new insights into the role of collagen in muscle protein synthesis. Researchers at Maastricht University in the Netherlands investigated how a protein mix of whey and collagen affects the formation of new muscle tissue – with notably positive results.
Why collagen is interesting for athletes
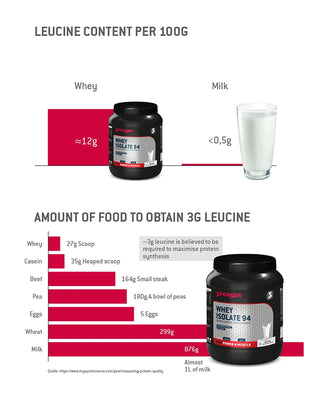
Collagen is widely recognised for its importance to skin and joint health, but it also constitutes a substantial component of the extracellular matrix within muscle tissue. This matrix plays a key role in force transmission, regeneration and the structural stability of muscles. While whey protein is known to stimulate myofibrillar protein synthesis (i.e. the formation of contractile muscle fibres), collagen has, until now, received little attention in the context of muscle development.
Study design and findings
Participants in the study consumed a protein shake containing a blend of whey protein and hydrolysed collagen. Researchers then measured the synthesis rates of two distinct protein types: myofibrillar protein (for muscle strength and volume) and muscle collagen (for structure and connective tissue). The results revealed a significant increase in both synthesis rates - greater than that observed with whey protein alone.
Combination of Whey and Collagen Supports New Muscle Tissue Formation
The combined intake of whey and collagen appears to promote the formation of both muscle protein and connective tissue, although to varying degrees. At rest, this protein mixture increases the build-up of both muscle protein (myofibrils) and connective tissue; after training, this is primarily the case with muscle protein (although there was a modest, non-significant rise in connective tissue synthesis).
Significance for sport, rehabilitation, and ageing
The findings suggest that collagen – particularly the amino acid glycine – plays a meaningful role in the development of connective tissue, thereby contributing to muscle regeneration and structural support. Whey protein, by contrast, continues to serve as the primary driver of conventional muscle growth. Collagen-enriched whey protein is likely to become more important in the future: on the one hand in strength training with a view to holistic muscle building, but on the other hand also for older people and rehabilitation patients when it comes to strengthening connective tissue, rebuilding muscle structure after injuries and counteracting muscle and tissue breakdown.
Literature
Aussieker T et al. (2025): Ingestion of a Whey Plus Collagen Protein Blend Increases Myofibrillar and Muscle Connective Protein Synthesis Rates, in: Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2025 Mar 1;57(3):544-554.